The possibilities of Design Thinking for addressing SDG strategies
Applied to the startup and business world, Design Thinking has shown us its effectiveness when proposing creative solutions in different areas. This is why, it is a well-suited methodology to address the challenges posed by the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals). It is another way of tackling the sustainability challenges in an ever-changing world.
What is Design Thinking?
It is a methodology which designs people-centred problem solving. In order to do this, it proposes a multidisciplinary vision. Thus, it integrates various tools, processes, mind maps and design techniques together with others which come from the social sciences, psychology or engineering. Its purpose is to identify, define and tackle the different challenges which, in each case, are addressed. Therefore, it is a methodology that uses multidisciplinary work teams.
Stages of Design Thinking applied to the SDGs
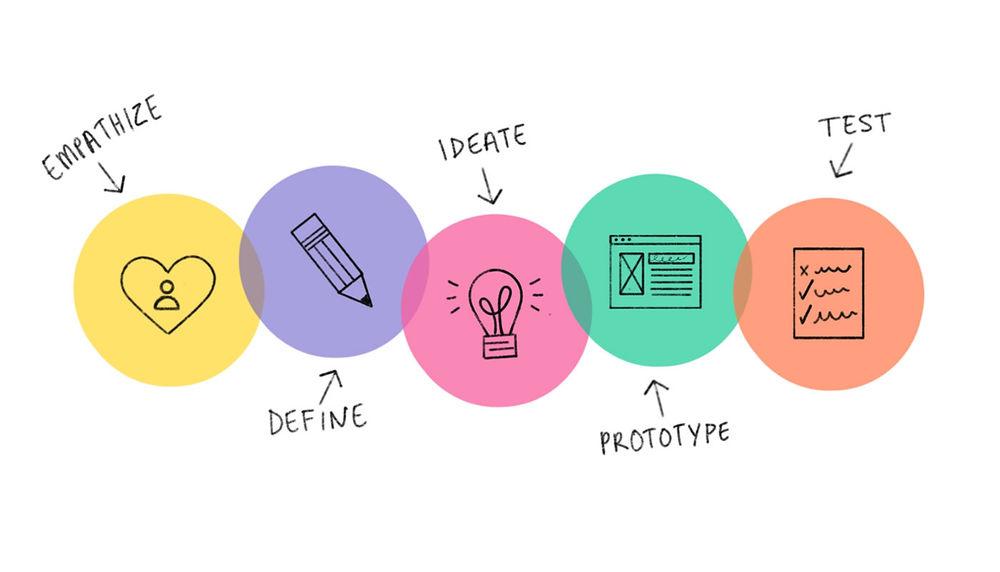
It is comprised of five stages:
- Empathize: It’s about understanding people’s needs, at a global level, the objectives you want to achieve and the obstacles you have in that respect. Being a collaborative methodology, it uses interviews and promotes the participation of the different actors. Ultimately, its function is for you to understand the reasons behind each SDG. If you do not have the opportunity to interact directly, the team must promote a comprehensive research approach.
- Define the exact problem: In so doing, you can invite the team to participate in outlining the hypothesis and put forward different solutions.
- Ideate: This methodology, promotes absolute freedom. This means that, in this stage, there are no correct or incorrect, good or bad ideas. In fact, it is the beginning of the creative process and, possibly, the first ideas are not the brightest. However, with patience, these will come. The ideal thing is to resort to brainstorming and write down what each person has proposed on a board. Think that one person’s idea might be the inspiration and ingenuity of another.
- Develop prototypes: These may take various forms. The aim is to test the validity of the ideas selected and their effectiveness. In order to do this, it is also useful to subject them to public judgement, since, other people outside the organisation may contribute their points of view.
- Evaluate: This stage is very important and should be continuously implemented. This way, the model you have developed with the team may be constantly improved. Only then will you come to the ideal final solution.
What does Design Thinking contribute to the SDGs?
It facilitates the initiation of sustainability strategies and promotes management change processes. This is very useful, particularly in governments and large companies. With which, it allows to adopt a better position which facilitates implementing the SDGs.
Its tools allow organisations to establish their own priorities and define strategies with the help of all their teams. Therefore, if you are in charge of sustainability in your company, you will have to focus on the following tasks:
- Align the SDGs with the organisation’s objectives.
- Involve all the employees in preparing the strategies and so opt for maximum creativity.
- Explain the result to the workers and management in each stage. In so doing, they will feel involved and commit themselves more to the project.
- Establish KPIs or key performance indicators.
Ultimately, Design Thinking is ideal for defining strategies conducive to achieving the SDGs. It is a methodology which, in addition to focussing on people, seeks innovative and creative solutions to complex problems, involving all parties. Therefore, it is very participative and favours the creation of strong bonds of complicity.
